At a glance
Official Name: Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia
Political system: Federal State with multi-party system
Capital City: Addis Ababa, which is also the seat of the African Union (AU) and United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (ECA).
Location: Ethiopia’s location gives it strategic dominance as a jumping off point in the Horn of Africa, close to the Middle East and Europe markets.
Area: 1.104 million square kilometres
Arable land: 513,000 square kilometres (45%)
Irrigated land: 34,200 square kilometres (3%)
Population: Estimation ~ 126 million (as of 2023)
Population density: Appx. 127 per square kilometer (2023)
Life expectancy: 64 years (men) 69 years (women)
Language: Afar, Amharic, Oromo, Somali, Tigrinya are the working language of the Federal Government.
GDP per capita: US$ 1027.6 (2022)
Climate: Temperate in the highlands, ranging from 20°C to 30°C (68°F to 86°F) and hot in the lowlands, often reaching 45°C (113°F). Rainfall ranges from 200 mm to 2000 mm.
Rainy Seasons: Abundant rain in June through August; mild rains in February and March.
Topography: Ethiopia has an elevated central plateau varying in height from 2,000 to 3,000 meters above sea level. In the North and center of the country there are some 25 mountains whose peaks reach over 4,000 meters. The most famous Ethiopia river is Blue Nile or Abbay, which flows 1,450 kilometres from its source to join the White Nile at Khartoum.
Currency: The currency of Ethiopia is based on the decimal system. The units of currency are the Birr and cents. The Birr is divided into 100 cents.
Working hours: Ethiopia is GMT+3. Government office hours are 8:30 am – 12:30 pm and 1:30 pm – 5:30 pm from Monday through Thursday; and 8:30 am to 11:30 and 1:30 pm to 5:30 pm on Fridays.
Country Profiles
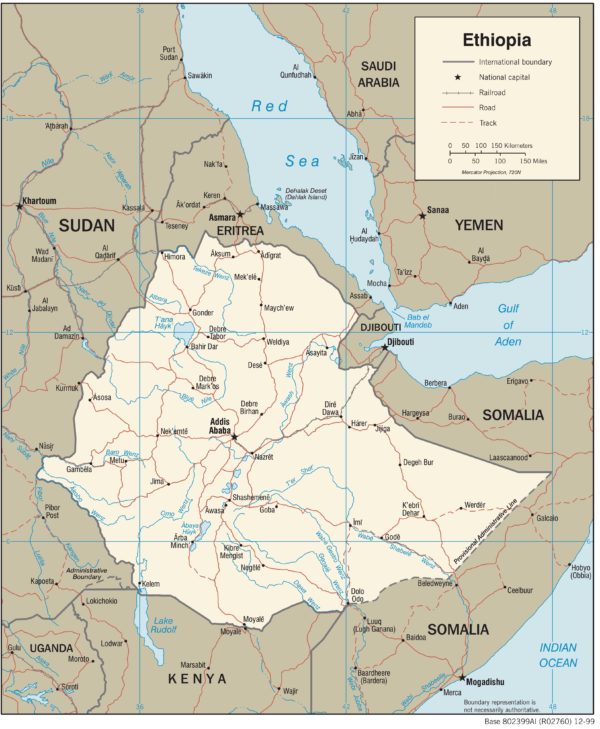
Ethiopia strategically located in the Horn of Africa. Its proximity to the Middle East and Europe, together with its easy access to the major ports of the region, enhances its international trade. Covering an area of approximately 1.14 million square kilometres (444,000 square mile), Ethiopia is bordered by the Sudan on the west, Somalia on the south-east, Djibouti on the east, Eritrea on the north and Kenya on the south.
Although Ethiopia lies within 15 degrees north of the equator, owing to the moderating influence of high altitude, the central highlands, where the vast majority of Ethiopian people’s live, generally enjoy temperate and pleasant climate, with average temperatures rarely exceeding 20 degrees centigrade. The sparsely populated lowlands, on the other hand, typically have sub-tropical and tropical climates. At approximately 850mm (34 inches), the average annual rainfall for the whole country is moderate by global standards. In most of the highlands, rainfall occurs in two distinct seasons: the “small” rains during February and March and the “high rains from June to September.
Federal Government
The Constitution of the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia establishes a federal parliamentary republic. The Federal Republic comprises of the Federal Government, the 12 autonomous Regional States and two city administrations. Both the federal and regional governments are organized into three branches of government – legislative, executive, and judicial.
The Federal legislative organ constitutes two houses: the House of People’s Representatives (HPR) and the House of Federation (HoF). The highest legislative authority is vested in the HPR whose members are elected by a plurality of votes cast in general elections every five years. The State Council is the highest organ of the state legislative authority.
The highest federal executive power rests with the Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers. The Prime Minister is the chair of the Council and the Commander-in-Chief of the National Armed Forces. The President, on the other hand, is the Head of State.
The Federal Supreme Court holds the highest judicial authority of the independent judiciary. The Court’s President and Vice President are nominated by the Prime Minister for appointment by the House of People’s Representatives.
Capital City
Addis Ababa, the Capital and largest city of Ethiopia, and lies on the central plateau at altitude varies from 2,000 to 2,600 meters above sea level; the centre is located at 2,300 meters, at the geographical location of 9° 1′ 48″ N, 38° 44′ 24″ E. The temperature is quite stable throughout the year. The average temperature of the coldest month (December) is15.5 °C (59.9 °F), that of the warmest month (April) is of 18. 8 °C (65.8 °F).
Young as cities go; Addis Ababa was founded in 1887 and the city’s population is estimated to be over 5 million. It is host to the African Union (AU), and the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (ECA). Several other international organizations have their headquarters and branch offices in the capital, which is also the centre of commerce and industry. Manufacturing plants for steel fabrication, wood, tanneries, textiles, cement, leather goods and breweries are among the activities located in and around Addis Ababa.
Ethiopia’s other important cities of trade and industry are: Awassa, Dire Dawa, Gondar, Dessie, Nazareth, Jimma, Harar, Bahir Dar, Mekele, Debere Markos and Nekemte. All these towns are connected to Addis Ababa by asphalt, highway and gravel roads, and most of them have good infrastructural facilities, such as first class hotels and airports. The Ethio-Djibouti railway connects Dire Dawa to the capital.
Local Time
Ethiopia is three hours ahead of Greenwich Mean Time. The 12-hour clock is sometimes used locally, and this can be confusing to visitors. The day starts with the sunrise i.e. the first cycle starts with “one O’clock” at 7 A.M. and goes on to “12 O’clock” at 6 P.M. The second cycle starts at 7 P.M. “one O’clock” and goes on to 6 A.M. “12 O’clock”.
Calendar
Ethiopia follows a slightly modified version of the Julian calendar, which consists of twelve months of thirty days each and a thirteenth month of five days (six days in a leap year). The calendar is eight years behind the Western (Gregorian) calendar from 11 September to 31 December and seven years in the rest of the year. The Ethiopian New Year is celebrated on the eleventh day of September. September 11, 2007, or 1 Meskerem 2000 (Ethiopian Calendar) marked the beginning of the Ethiopian third millennium.