This article was originally published in the 6th issue (April 2017) of the The Ethiopian Messenger, the quarterly magazine of the Embassy of Ethiopia in Brussels.
Ethiopia is blessed with many advantages when it comes to horticulture. In the span of ten years, the country was able to transform its flower sector from a tiny sector into a 225 million dollars cut flowers export business with many opportunities for further growth.
Since the downfall of the Derg regime in 1991, the economic policies and strategies of the Government of the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia have brought about enormous developments in the economic sector. Horticulture can be counted as one of these success stories, as Ethiopia has transformed its flower sector from a tiny sector into a 225 million dollars cut flowers export business within a span of ten years.
Until recently, the Ethiopian horticulture sector was mainly based on traditional agriculture. The introduction of mechanized agricultural practices boosted the growth of the industry, which has now become a significant contributor to national export earnings, and to the private sector development in the country.
Favourable conditions for horticulture
Ethiopia is blessed with many advantages when it comes to horticulture. The country has a favourable climate with diverse agro-climatic zones and long growing seasons which offer ideal conditions for growing a wide array of fruits, vegetables, flowers, spices and herbs. Moreover, about 12,797 hectares of suitable land is available for horticulture, with only 11 percent of this surface is already used for horticulture. Finally, a large workforce is available. The sector has already created about 183,000 jobs, out of which 70 percent are for women.
Other advantages include readily accessible water for irrigation (including 125 billion cubic meters of surface water and 2.6 billion cubic meter of ground water), cold chain facilities at three international airports (Bole, Bahir Dar and Hawassa), an extended rail transport network and the incentive package provided by the government, that have all contributed to the phenomenal growth of the horticulture sector in the last decade.
Overview of the sector’s growth
The Ethiopian horticultural sector is composed of fruits, vegetables, flowers, herbs and spices. Although the sector is only about a decade old, mechanized horticulture production has shown a great increase in farm number, revenue generation and volume of export. There are currently over 130 investments in the sector, made up of local investors (56), foreign direct investors (64) and joint venture partnership (10). Flower farms occupy 1,426 hectares, while fruits and vegetables take up 11,371 hectares. The sector provides employment for approximately 183,000 persons and has been growing exponentially, generating 275 million dollars in 2015-2016 compared to 28.5 million dollars in 2004-2005. This makes the sector the fifth largest foreign revenue generator for the country.
Floriculture
Ethiopia now has over 130 active flower-growing farms and is the fourth largest non-EU exporter of cut-flower to the European Union and the second largest flower exporter from Africa. Floriculture has contributed to 225 million dollars, or 80 percent of the total foreign revenue earning of the sector. The majority of the production is made of roses (about 80 percent of the production), and the country is noted for the high quality, long stems, large buds and vibrant colour of its roses. In addition to the rose farms, five farms are engaged in the production of cuttings and eight farms produce a variety of other types of flower crops, including gypsophilia, hypericum, limonium, chrysanthemum, carnations, static, pot plants and a range of summer flowers.
Fruits
Ethiopia has a long history of producing fruits in a traditional way for home consumption and export to neighbouring countries. The main fruits produced and exported by the country are mangoes, banana, papaya, avocados, citrus and pineapple. However, recent larger scale investments in fruit growing have favoured the production of new crops such as strawberries, table grapes and passion fruits, and in addition pears, plums as emerging fruits. There are currently eight operators engaged in large scale and nontraditional fruit crop production, which is seen as an area that has enormous potential for development.
Vegetables
Vegetables grown in Ethiopia include, among others, green beans, snow peas, broccoli, asparagus, cherry tomatoes, cauliflower, eggplant and cucumber, onion and garlic. Much of the land available for growing fruits and vegetables in the country is suitable for organic certification. In 2014, there were 22 vegetable farms throughout the country – 16 owned by local entrepreneurs, five financed by foreign direct investments, and one joint venture.
Herbs and spices
The major spices cultivated in Ethiopia are ginger, hot pepper, fenugreek, turmeric, coriander, cumin, cardamom, and black pepper. Close to 122,700 hectares are being used for spice farming, with spice production reaching 244,000 tonnes per year. Potential areas for the cultivation of spices are the regions of Amhara, Oromia, Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples’ Region and Gambella Region. The total potential for lowland spice farming is estimated to be 200,000 hectares. The companies already engaged in spices and herbs are highly productive and produce over 21 varieties of herbs and herbs for local consumption and export as fresh product to many international market destinations. Production standards are high and all investors in this sector comply with the Good Agricultural Practice and Food Safety Standards required for food crops entering the European market.
Market proximity and destination
In addition to its many natural gifts, Ethiopia benefits from its location, close to the markets of Europe and the Middle East, and possesses good freight links to all major and emerging markets including Western Europe, the Middle and Far East, Russia and the USA.
Currently, Ethiopian floriculture is mainly exported to the Netherlands (80.3 percent), but exports extend to France, Germany, Italy, Canada, Norway, Belgium, Sweden, UK, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Japan, USA and other EU countries.
Fruits and vegetables have traditionally been exported by road to neighbouring countries, Somalia (56.8 percent), Djibouti and the Sudan, but increasing quantities are now also being shipped by air to the Netherlands, the UAE, the United Kingdom, Germany, Belgium, Russia and Yemen. The new fast track electric-powered railway line connecting Addis Ababa to Djibouti, other railway lines under construction and improvements to the internal highway roads will also open up opportunities for road or rail transport of production to the coast, and then sea freight to a range of market destinations.
Development of new horticulture hubs
With the aim of accelerating the transformation of the horticulture industry, the Ethiopian government established new horticultural hubs at four geographical locations: Alagae, Arbaminch, Bahir Dar and Hawassa, which are conducive for investment. The four horticulture hubs identified have several competitive advantages (see table below).
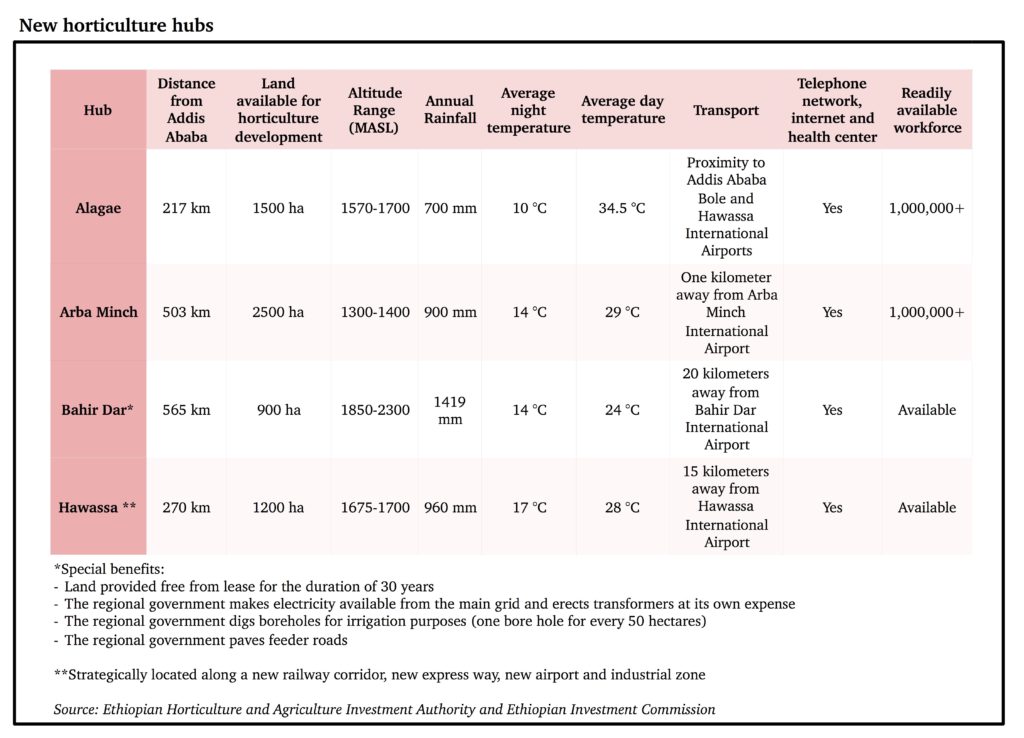
Incentives applicable to new horticulture hubs
Investors in horticulture have zero tax privilege on exports. They are exempted from income tax for 8-10 years and from duties and other taxes on imports of machinery, construction materials, spare parts, raw materials and vehicles and provided with a one-stop government services and essential infrastructure. They have access to finance with loan facilities (up to 70 percent of the total investment) from the Development Bank of Ethiopia, with 30 days of loan approval and readily allocated finance. They benefit from aboundant land and water, with over 6,000 hectares of available land, 30 years of zero charge land lease, 15 days of handover period and abundance of ground and surface water.
In terms of logistics, the national carrier, Ethiopian airlines, flies to over 98 destinations worldwide both on freighters and belly hold, with state-of-the art cooling facilities specialized in handling horticulture products.
A responsible and sustainable industry
People who invest in horticulture in Ethiopia have to respect corporate social responsibility, Integrated Pest Management, code of practice and provide employment to local people.
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is the farm’s sense of responsibility towards the community and environment (both ecological and social) in which they operate. It includes support of medical care via construction of farm clinics or hospital, support for education by providing training to the staff, support for construction of local schools, provision of water in rural areas, affordable meals for employees and rehabilitation. Most farms fund these activities from their farm revenue and some farms are also certified by Fair Trade labels.
Integrated Pest Management, including the use of Biological Controls makes an important contribution to operator safety, the protection of the environment and the production of safe food. Many farms are applying this principle and the
Crop plantation in Ethiopia
Ethiopian Horticulture Producers and Exporters Association (EHPEA) closely works with the members of the association, the government and other stakeholders.
The EHPEA code of practice introduced in 2007 has been revised and upgraded on several occasions to reflect the increasing requirements of the market and the need to maintain continuous improvement on the farms. The Code contains requirements for Good Agricultural Practices, Protection for the Environment, Employment Conditions and Staff Safety and Welfare. The benchmarking Version is 4.0 of the Code with Global GAP and the Global Social Compliance Program with a view to achieving full market recognition for the standard and reducing the audit burden on farms supplying multiple clients in the international market. EHPEA is committed to standards and employs a Team of Trainers to provide training, advice and support for farms to meet Code and other Market Label standards. In addition to contributing to the overall economic development of the country, the horticultural export industry has created job opportunities for about 183,000 people, 70 percent of whom are women. This is an important contribution to local economy, to the empowerment of women in the community and to household food security.
In a nutshell, looking into the untapped and lucrative opportunities and incentive packages given to the industry, foreign direct investors and the Ethiopian diaspora are invited to invest in Ethiopia in the sector in general, and in the four identified new horticulture hubs in particular, to enjoy the benefits of this growing industry.
The Federal and regional institutions responsible for the horticulture sector development in Ethiopia are: Ethiopian Horticulture and Agriculture Investment Authority, Ethiopian Investment Commission, and Investment Commissions of respective Regional States. The Ethiopian Horticulture Producers and Exporters Association is a pioneer horticulture legal entity representing actors in the sector.
References: Ethiopian Horticulture Producers & Exporters Association (EHPEA); Ethiopian Investment Commission (EIC) database of licensed projects; All Africa “Ethiopia: Revenue of Horticulture Export Increasing”, 26 December 2014.